info@dentallifeline.com
Blog
Dental Night-guards : Your Silent Protector While You Sleep
If you often wake up with jaw pain, headaches, or tooth sensitivity, your teeth might be working overtime while you’re asleep.
The culprit?
- Bruxism — the habit of grinding or clenching your teeth at night. Over time, this can wear down your enamel, cause fractures, and even affect your jaw joints. Luckily, there’s a small but mighty solution: the dental nightguard.
What is a Dental Nightguard?
A dental nightguard is a custom-made appliance that fits over your teeth, creating a protective barrier between your upper and lower jaws. Think of it as a safety helmet for your teeth while you sleep – it absorbs the pressure
and prevents tooth-to-tooth contact.
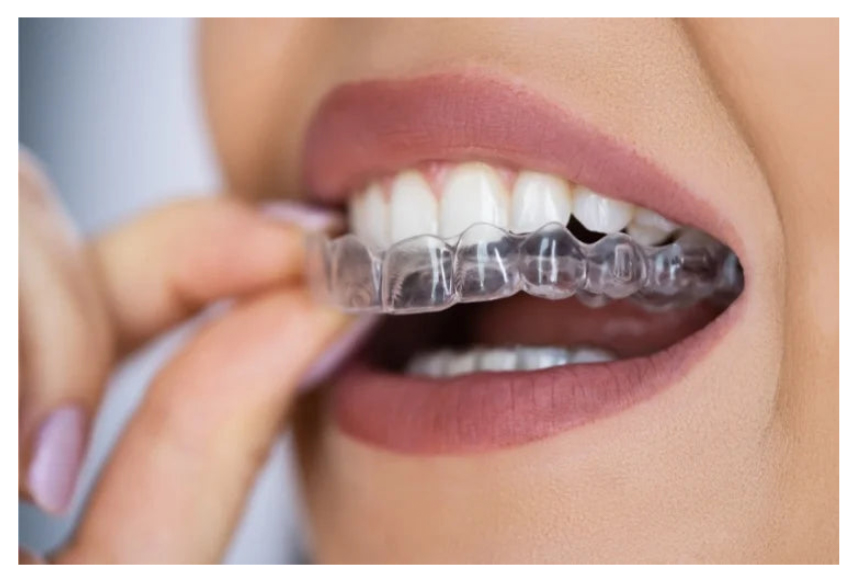
Why You Might Need One
To Prevent Tooth Damage Constant grinding can lead to chips, cracks, and worn-down teeth. A nightguard helps prevent irreversible enamel loss.
To Relieve Jaw Pain
By reducing pressure on the jaw muscles, a nightguard can ease morning soreness and tension.
To Protect Dental Work
If you’ve invested in crowns, veneers, or implants, a nightguard helps prolong their life by shielding them from excessive force.
To Reduce Headaches
Bruxism-related headaches often improve when the jaw muscles get a break from constant clenching.
Custom vs. Over-the-Counter Nightguards
Custom Nightguards: Made by your dentist from a precise mold of your teeth. They fit comfortably, last longer, and offer the best protection.
Over-the-Counter Nightguards: Available at pharmacies, often cheaper, but may be bulky or less effective due to poor fit.
Caring for Your Nightguard
- Rinse with cool water after each use.
- Brush it gently with a soft toothbrush—no toothpaste, as it can be abrasive.
- Store in a ventilated case.
- Avoid heat (hot water, sunlight) to prevent warping.
Final Thoughts
A dental nightguard may seem like a small addition to your bedtime routine, but it can save you from costly dental treatments and chronic discomfort. If you suspect you’re grinding your teeth at night, don’t wait for damage to show—talk to your dentist about getting a nightguard.
Your smile will thank you in the morning.
 24 Feb 2025
24 Feb 2025
Diseases Related to Gums: A Comprehensive Guide
Gum diseases, also known as periodontal diseases, affect the tissues surrounding and supporting your teeth. These conditions range from mild irritation (gingivitis) to more severe infections (periodontitis) that can lead to tooth loss. In this blog, we will explore the types of gum diseases, their symptoms, causes, diagnosis, management, prevention, prognosis, and possible complications.
Types of Gum Diseases
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease. It is an inflammation of the gums that usually occurs due to poor oral hygiene. If not treated, gingivitis can progress to more serious gum diseases.
- Periodontitis: Periodontitis occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. It involves inflammation not only of the gums but also of the tissues and bone that support your teeth. It is a severe gum disease that can result in tooth loss if not treated.
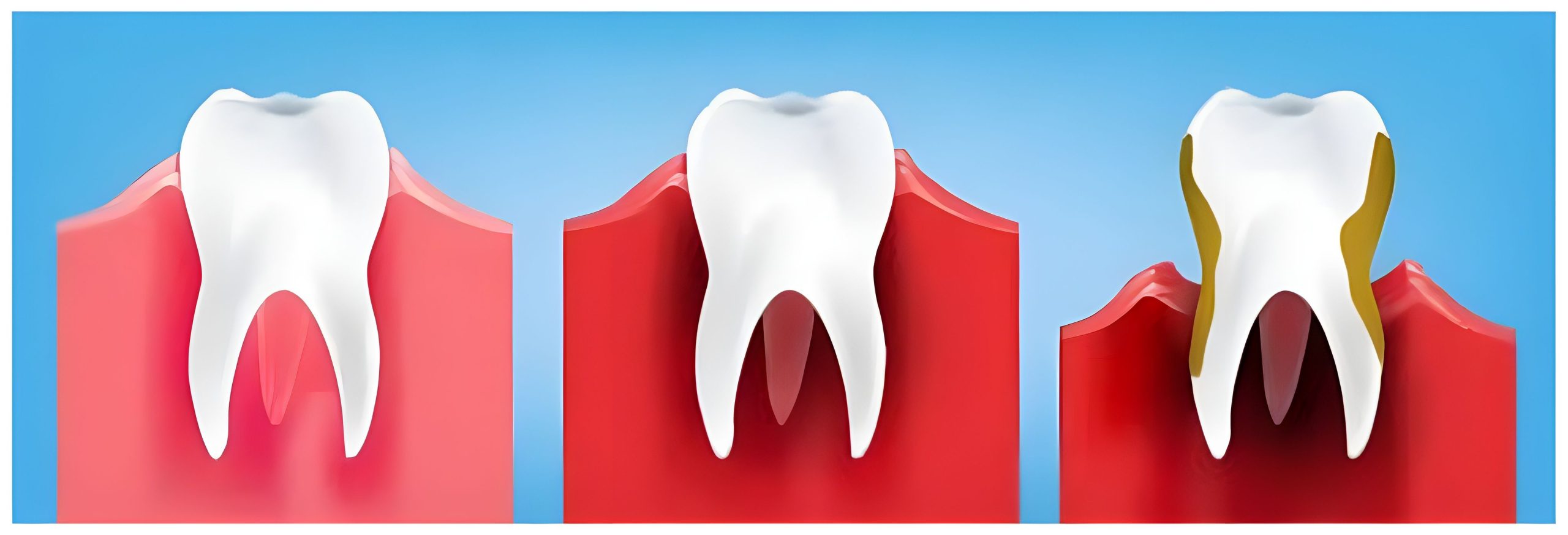
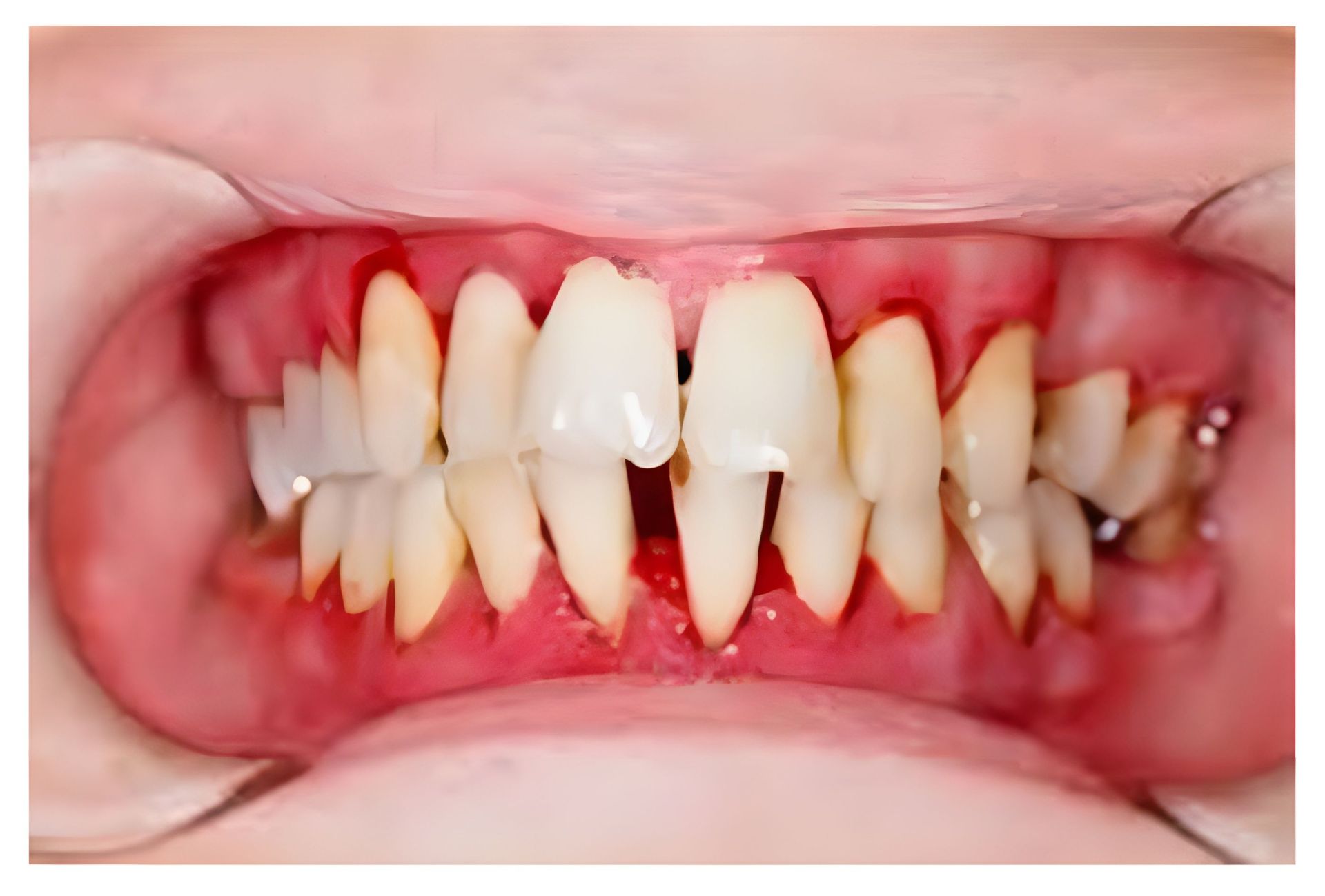
Symptoms of Gum Diseases
Gingivitis:
- Red, swollen, and tender gums
- Bleeding gums when brushing or flossing
- Bad breath
- Receding gums
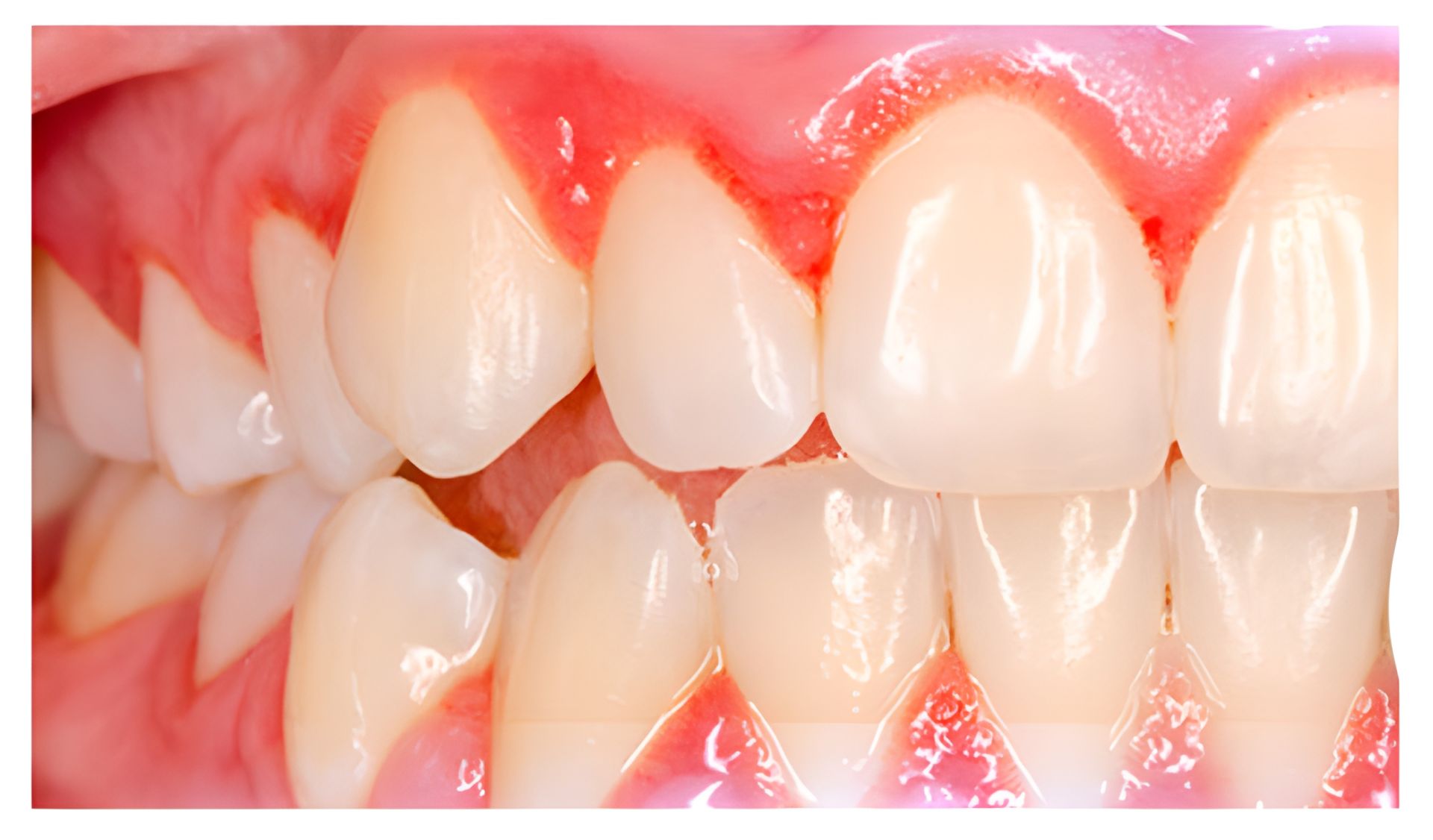
Periodontitis:
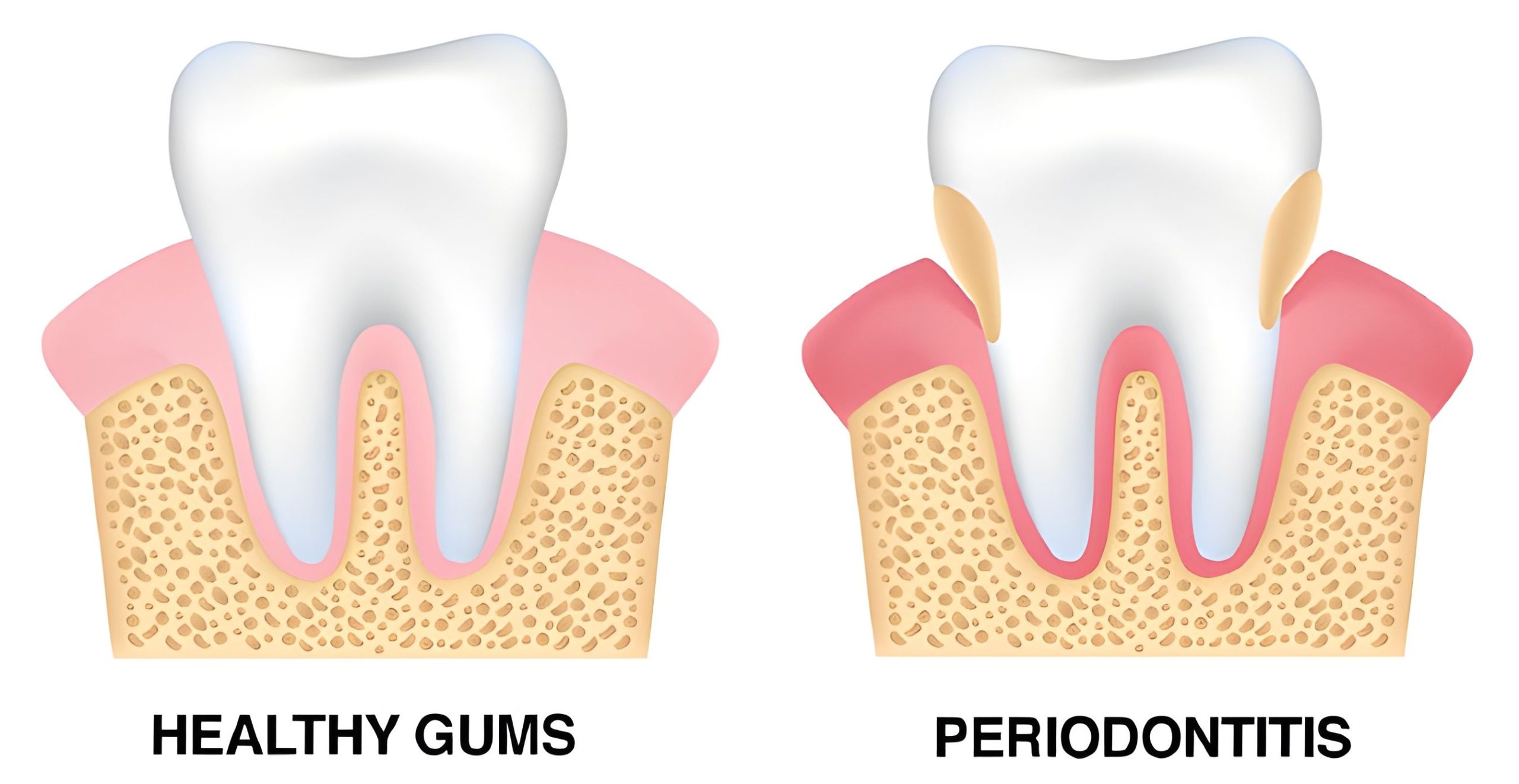
- Gingival symptoms (red, swollen gums)
- Gums that pull away from teeth, creating pockets
- Loose teeth or changes in bite alignment
- Pain while chewing
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
Causes of Gum Diseases

- Poor Oral Hygiene: The main cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene that encourages plaque to form on teeth, which can lead to gingivitis Plaque is a sticky, colourless film of bacteria that builds up on your teeth.
- Smoking or Chewing Tobacco: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk of gum disease by weakening the immune system and damaging gum tissue.
- Poor Nutrition: Lack of essential nutrients, especially vitamin C, can impair the body’s ability to fight infections and may contribute to gum disease.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Diseases like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer treatments may interfere with the body’s ability to fight infections, making the gums more susceptible to gum disease.
- Medications: Some medications can affect the health of your gums, leading to symptoms like dry mouth or abnormal gum growth.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, menstrual cycle, or menopause can make gums more sensitive, increasing the risk of gum disease.
- Genetics: A family history of gum disease can increase your likelihood of developing it.
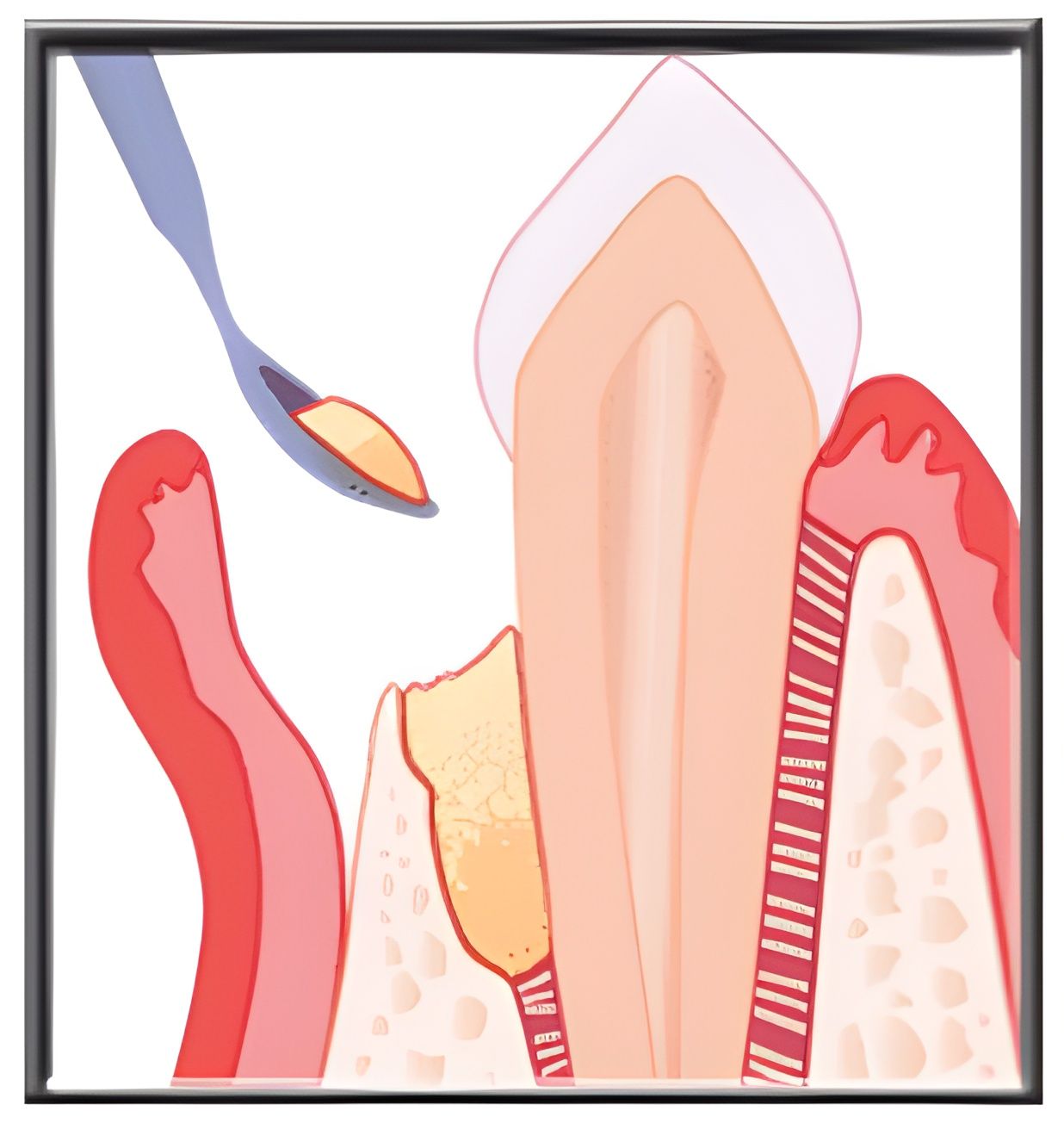
Diagnosis of Gum Diseases
Diagnosis of gum diseases typically involves a dental exam. Your dentist will check for signs of inflammation, pocket depth between teeth, gum recession, and tooth mobility. They may also:
- Take X-rays: To determine the extent of bone loss caused by periodontitis.
- Gingival Crevicular Fluid Test: In advanced cases, this fluid may be analysed to detect the presence of bacteria causing gum infection.
Management of Gum Diseases
For Gingivitis:
- Professional Cleaning: A dentist or dental hygienist will clean your teeth to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing, as well as using mouthwash, can
help reverse gingivitis.
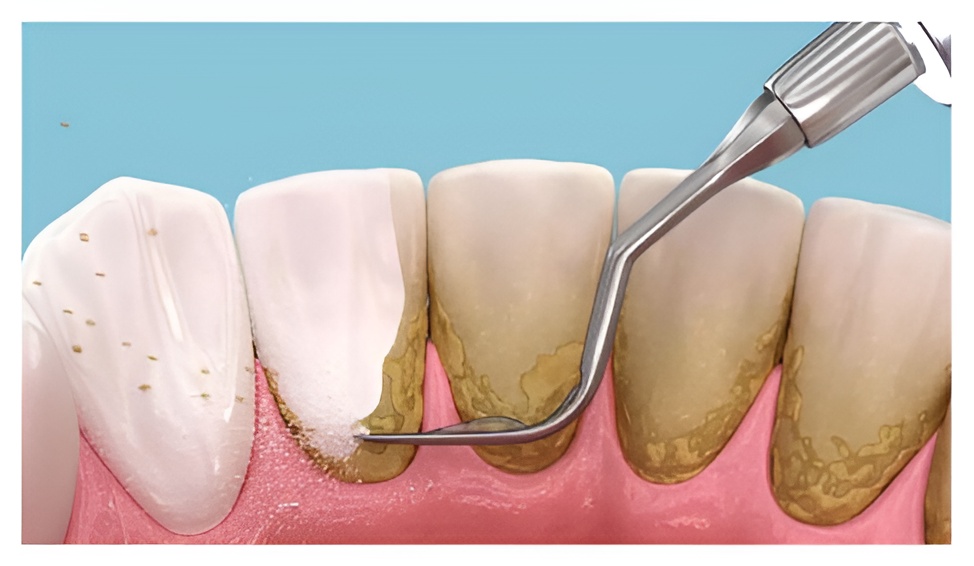

For Periodontitis:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning treatment removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the root surfaces to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
- Antibiotics: Your dentist may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics to help control infection.
- Surgical Treatments: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as flap surgery or bone grafting may be necessary to restore lost bone or tissue.
Prevention of Gum Diseases
- Regular Brushing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque and food particles.
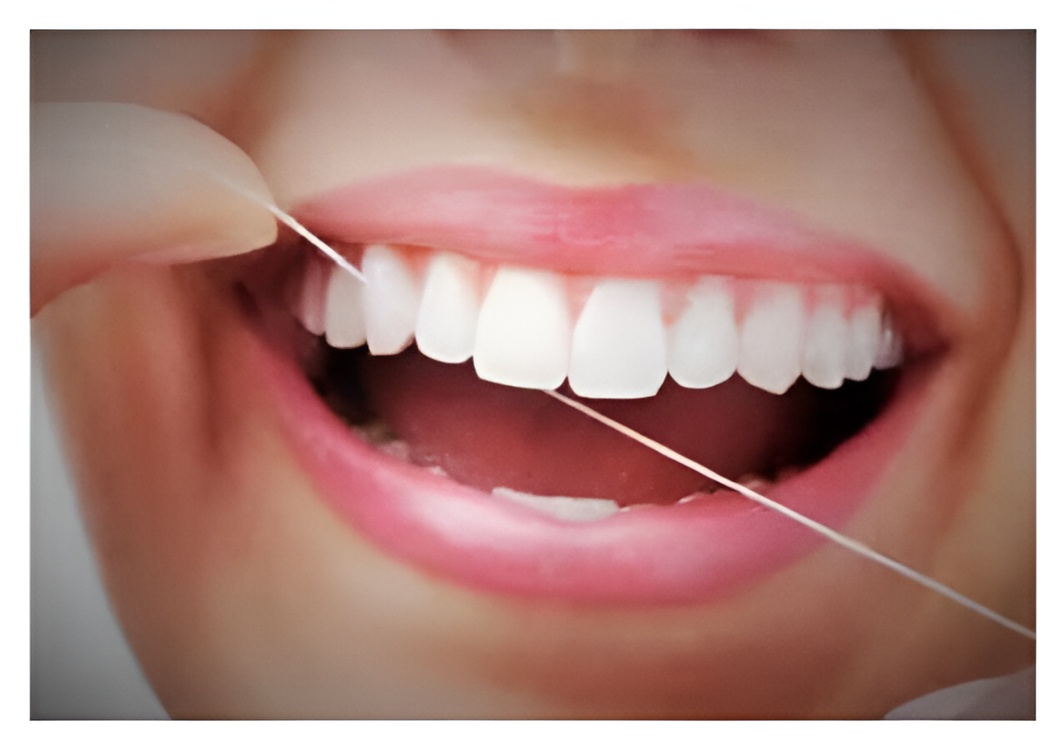
- Flossing: Floss daily to clean between your teeth and below the gumline where a toothbrush can’t reach.
- Regular Dental Visits: Visit your dentist for routine checkups and cleanings, ideally every six months.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease, so quitting can significantly reduce your risk.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially Vitamin C, to help your body fight off infections.

Prognosis of Gum Diseases
- The prognosis for gum diseases largely depends on early detection and intervention. Gingivitis, when treated early, can be reversed, while periodontitis can be managed but not completely cured. With appropriate treatment and diligent oral care, most individuals with gum disease can manage the condition and prevent further damage.
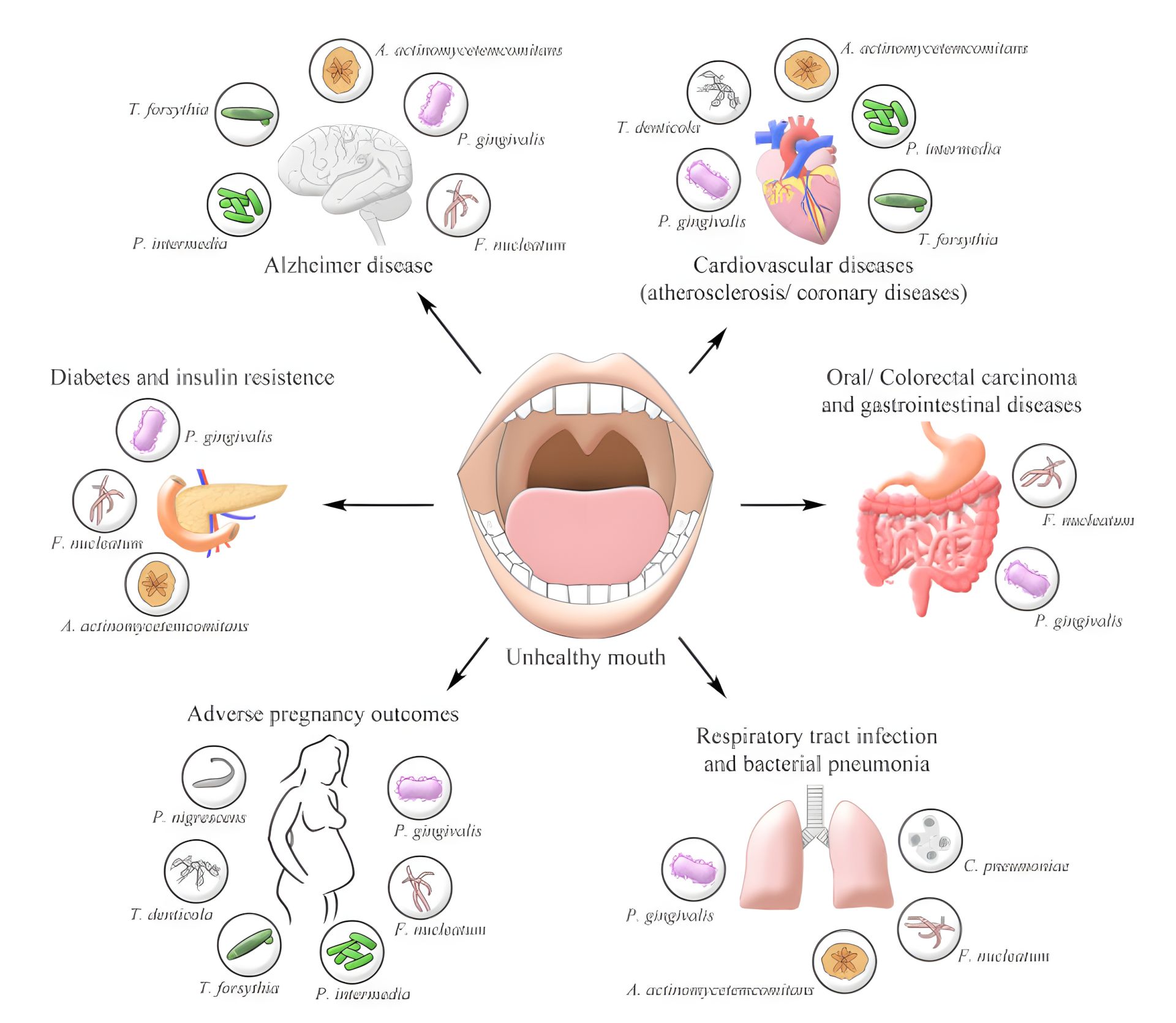
However, if left untreated, gum disease can lead to severe consequences like tooth loss, infections that spread to other parts of the body, and increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Complications of Gum Diseases
- Tooth Loss: Severe periodontitis can lead to the destruction of the bone that supports your teeth, causing them to loosen and eventually fall out.
- Heart Disease: Gum disease has been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Inflammation caused by gum disease may contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions.
- Respiratory Infections: Bacteria from the gums can enter the respiratory system, leading to pneumonia and other lung infections.
- Diabetes Complications: Gum disease can make it more difficult to control blood sugar, making it more challenging for people with diabetes to manage their condition.
- Pregnancy Risks: Pregnant women with gum disease may face complications like preterm labor and low birth weight.
Conclusion
Gum diseases are serious conditions that can affect not only your oral health but your overall well-being. Recognising the symptoms early and practicing good oral hygiene can go a long way in preventing and managing gum disease. Regular dental visits and lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and eating a healthy diet, are crucial for maintaining healthy gums. By staying proactive about your dental care, you can ensure that your gums remain healthy for years to come.
Remember, a healthy mouth leads to a healthy body!
 24 Jan 2025
24 Jan 2025
Fluoride and Its Implications in Dentistry: A Comprehensive Overview
Fluoride has long been a topic of discussion in the field of dentistry due to its essential role in promoting oral health. Its use in preventing tooth decay and enhancing overall dental hygiene has been a revolutionary advancement, benefiting millions of people worldwide. This blog will explore fluoride’s significance in dentistry, its benefits, potential concerns, and its broader implications.
What is Fluoride?
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that can be found in soil, water, and various foods. In dentistry, fluoride is primarily used in topical forms—such as toothpaste, mouth rinses, and professional treatments administered by dental providers—to help prevent cavities and promote healthy teeth.
The Role of Fluoride in Preventing Tooth Decay
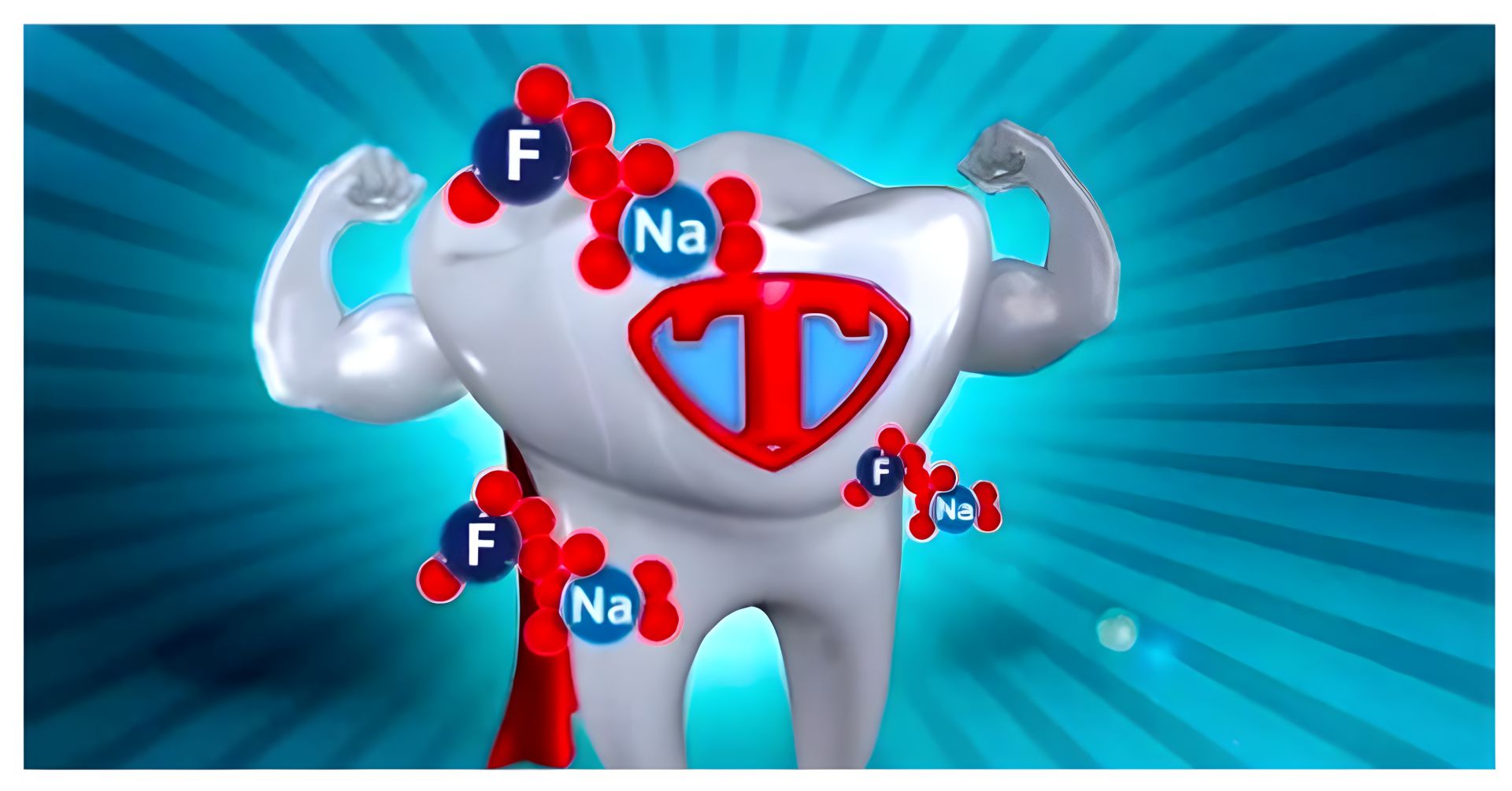
Tooth decay, or dental caries, is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide. It occurs when acids produced by bacteria in the mouth erode the tooth enamel, leading to cavities. Fluoride plays a crucial role in the prevention of tooth decay by:
-
1. Remineralising Enamel: Fluoride helps to remineralise the tooth enamel that has been demineralised by acids. This process restores essential minerals like calcium and phosphate to the enamel, making it stronger and more resistant to future decay.
2. Inhibiting Bacterial Growth: Fluoride inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, reducing the amount of acid produced by these bacteria after they feed on sugars and carbohydrates.
3. Reducing Cavities: Numerous studies have demonstrated that fluoride use reduces the incidence of cavities. This is particularly evident in populations that receive fluoridated drinking water, which has contributed to a significant decline in dental decay over the years.
Fluoride Treatments in Dentistry
Fluoride treatments in dentistry are designed to deliver higher concentrations of fluoride to the teeth, offering enhanced protection against cavities and promoting better oral health. There are several types of fluoride treatments commonly used by dental professionals:
-
1. Topical Fluoride Treatments
These treatments are applied directly to the teeth and are the most common form of fluoride use in dentistry. They include:
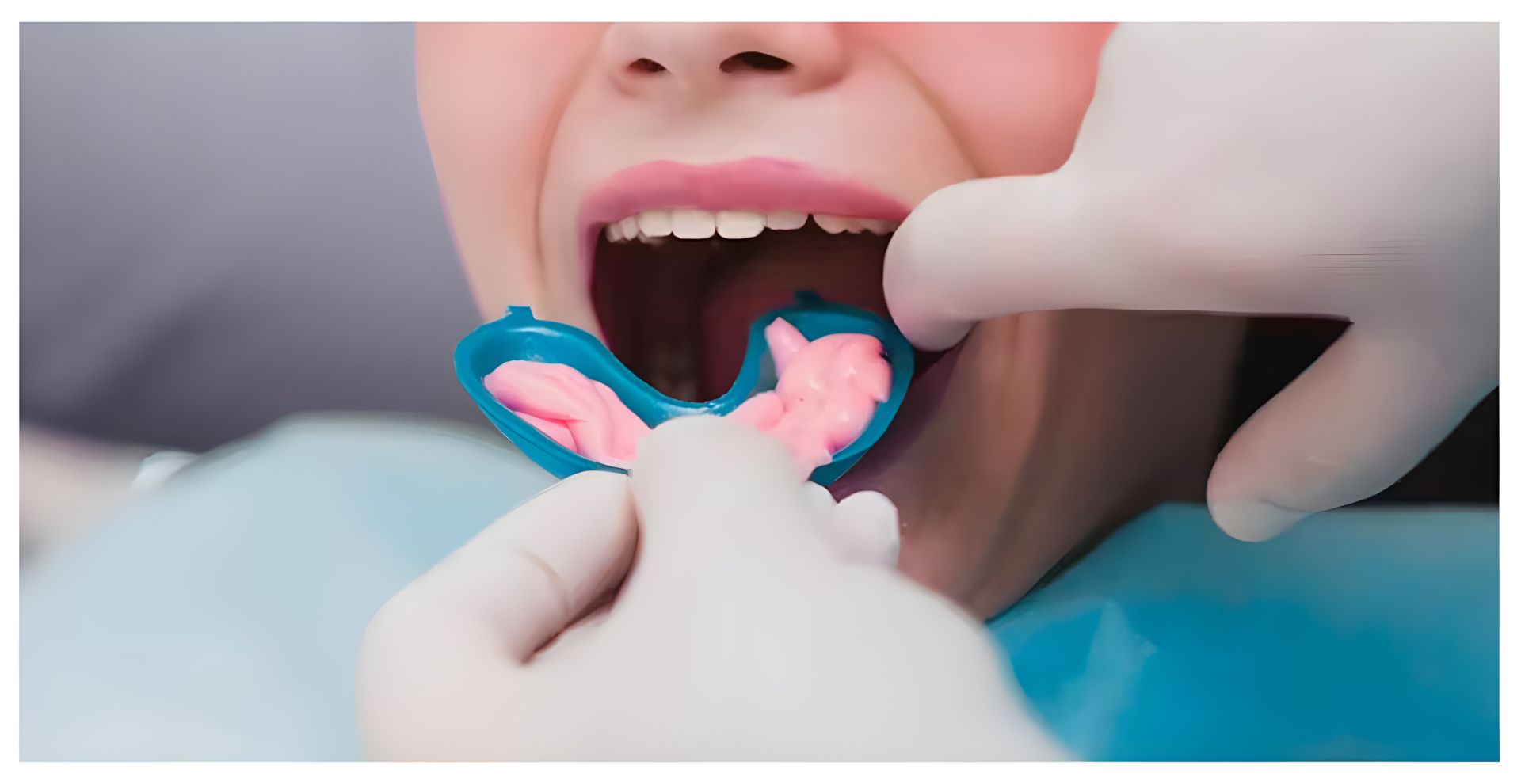
– Fluoride Varnishes: This is one of the most popular methods of fluoride treatment used by dentists. Fluoride varnishes are applied to the surface of the teeth during routine check-ups. The varnish hardens quickly, allowing it to remain on the teeth longer than other forms of fluoride, providing more time for the fluoride to remineralise enamel. This treatment is especially effective in children and individuals at higher risk for cavities.
– Fluoride Gels and Foams: Fluoride gels or foams are applied to the teeth using a tray that fits over the teeth for a few minutes. These treatments are more commonly used for children and people with special needs who may benefit from a higher fluoride concentration. These treatments are highly effective in reducing cavities, especially in areas with limited fluoride exposure from water sources.
-
2. Fluoride Rinses
Fluoride mouth rinses are an easy and effective way to deliver fluoride to the teeth. These are typically available over-the-counter in lower concentrations or by prescription for higher-strength formulas. Rinses are recommended for individuals who may be at higher risk for cavities, including those with dry mouth, braces, or a history of frequent tooth decay. Daily use of fluoride rinses can further help protect against plaque buildup and tooth sensitivity.
-
3. Fluoride Toothpaste

While not a professional treatment, fluoride toothpaste is one of the most accessible ways for individuals to maintain fluoride exposure on a daily basis. The fluoride in toothpaste helps reduce plaque, strengthen tooth enamel, and prevent cavities. It’s recommended that people use fluoride toothpaste twice daily to maintain optimal oral health.
Benefits of Fluoride in Dentistry
The benefits of fluoride in dentistry are well-documented and include:
-
– Cavity Prevention: Fluoride is most renowned for its ability to reduce the risk of cavities. It helps strengthen tooth enamel and makes it more resistant to acids and plaque buildup, reducing the overall prevalence of dental decay.
– Cost-Effective: Fluoridated water and fluoride treatments are cost-effective ways to combat tooth decay. Preventing cavities with fluoride can significantly reduce the need for costly dental procedures, saving individuals and healthcare systems money in the long run.
– Improved Oral Health for All Ages: Fluoride benefits people of all ages, from children who are still developing their teeth to adults and seniors. Fluoride’s protective effects help prevent cavities and tooth sensitivity across the lifespan.
– Reduction of Disparities in Oral Health: Fluoridation in community water supplies can help reduce oral health disparities in underserved populations, providing equitable access to cavity prevention, particularly in areas where access to dental care may be limited.
Potential Concerns and Risks of Fluoride
While fluoride has many proven benefits, there are also some concerns regarding its use, particularly in excessive amounts. These risks are rare but worth noting:
1. Dental Fluorosis: One of the primary concerns of fluoride overuse in children is dental fluorosis, a cosmetic condition that results in white spots or streaks on the teeth. This condition typically occurs when young children swallow toothpaste or mouth rinse that contains fluoride. In severe cases, fluorosis can lead to pitting or staining of the teeth.
2. Skeletal Fluorosis: Excessive exposure to fluoride over a long period can lead to skeletal fluorosis, a condition that affects bones and joints. This is extremely rare in areas where fluoride levels in water are within safe limits.
3. Debates Over Fluoridation: Some people have raised concerns about the potential health risks of water fluoridation, citing studies that suggest links to conditions such as thyroid problems, cancer, and developmental issues. However, the overwhelming consensus from public health organisations, including the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organisation (WHO), is that fluoridated water is safe at recommended levels.
The Future of Fluoride in Dentistry
As research continues, new fluoride delivery methods and treatments are being developed to further enhance its benefits. Innovations in fluoride varnishes, more effective fluoride-releasing dental materials, and personalised treatments are helping dentists provide better care for their patients.
Additionally, as the conversation about fluoridation continues, communities and policymakers must weigh the benefits of fluoride in public water supplies with public concerns, ensuring that fluoride levels remain safe and effective.
Conclusion
Fluoride has proven to be a cornerstone in modern dentistry, providing significant protection against tooth decay and promoting overall oral health. From its role in remineralising enamel to its widespread use in community water fluoridation, fluoride continues to be a powerful tool in the fight against dental caries. While it is essential to be mindful of the risks associated with excessive fluoride use, when applied appropriately, fluoride offers a safe and effective way to preserve and improve dental health for individuals of all ages.
As more advancements in fluoride technology emerge, it’s likely that its role in oral health will continue to evolve, further cementing its place as one of the most beneficial and accessible dental treatments available.
